Achilles Tendinitis
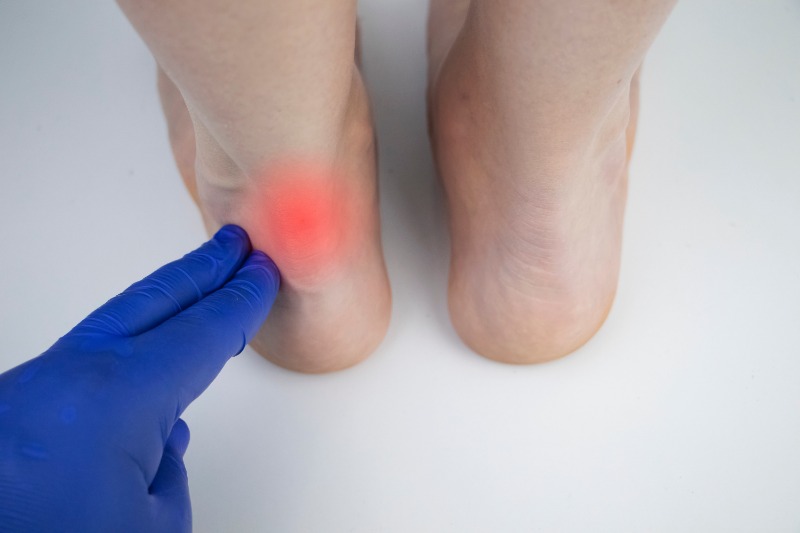
Achilles Tendinitis
Achilles tendinitis affects the largest tendon in the body, the Achilles tendon. This type of injury typically occurs because of overuse. The main function of the Achilles tendon is to transmit power from the calf muscles to the heel and the foot. When this tendon is harmed, it can be extremely painful and may lead to further complications including tears, ruptures, tendinitis, peritendinitis, tendinosis, tendinopathy, and bursitis.