By Aarti Kumar, DPM, AACFAS, DABPM
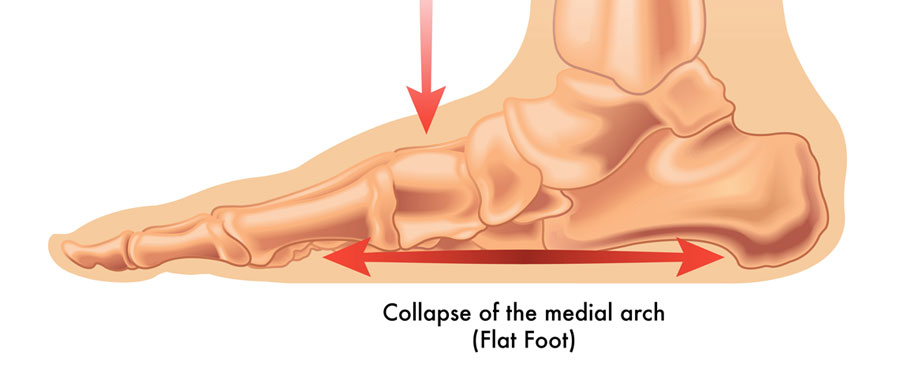
Pes planovalgus is a medical term used to describe a common foot deformity where the arch of the foot collapses and the foot rolls inward at the ankle. This condition is sometimes referred to as “flat feet” or “pronated feet”.
Pes planovalgus can be a congenital (present from birth) condition or can develop over time due to various factors; such as genetics, ligamentous laxity, injury, obesity or the natural aging process. Some common symptoms and characteristics of pes planovalgus include: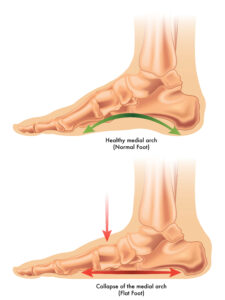
- Flattening of the arch of the foot
- Pain or discomfort in the foot, especially in the arch or heel
- Ankle pain or instability/feeling of ankles falling in
- Overpronation, where the foot rolls too far inward during walking or running
- Inward tilting of the heel bone and knocking of the knees
- Abnormal shoe wear patterns
Treatment for pes planovalgus may include:
- Orthotic devices: Custom or over-the-counter shoe inserts can provide arch support and improve foot alignment.
- Supportive footwear: Wearing shoes with good arch support and stability can help relieve discomfort and prevent the condition from worsening.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to strengthen the muscles around the foot and ankle can help improve stability and alleviate symptoms.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy body weight can reduce the strain on the feet.
- Rest and ice: These can help manage pain and inflammation.
- In some cases, when conservative treatments are ineffective, surgery may be considered to correct the deformity.
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional if you suspect you have pes planovalgus or are experiencing foot pain, as they can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend the most appropriate treatment for your specific situation.