By Pedram A. Hendizadeh, DPM, FACFAS
Introduction:
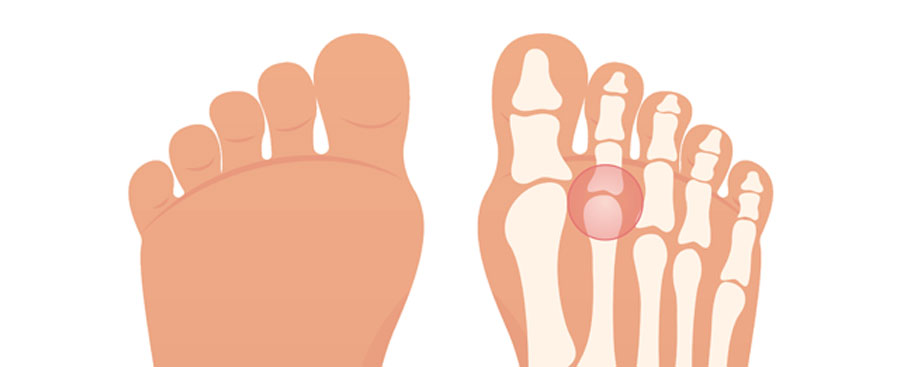
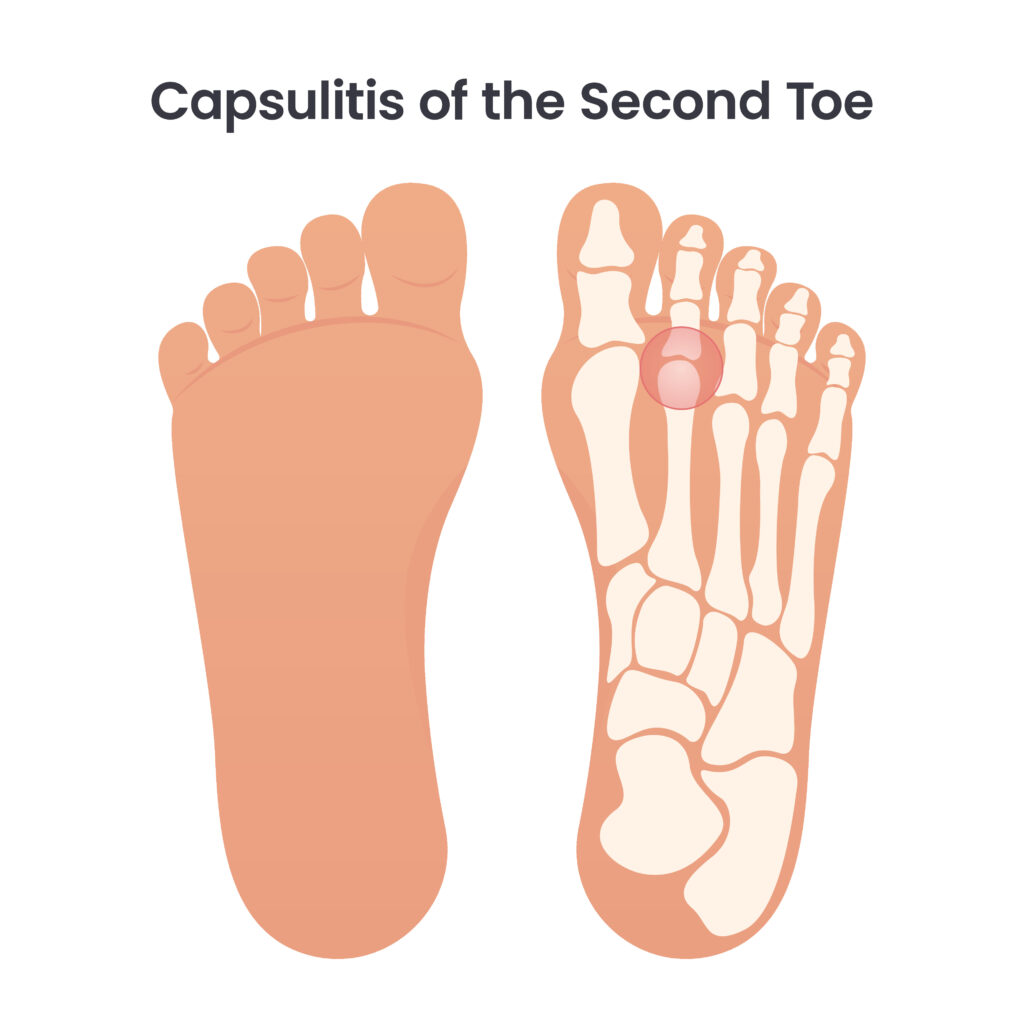
Capsulitis of the second metatarsophalangeal joint is a common condition that affects the forefoot. It occurs when the joint capsule, a fibrous structure that helps stabilize the joint, becomes inflamed and painful. This condition often presents with symptoms such as pain, swelling, and difficulty walking.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Capsulitis can be caused by repetitive trauma, biomechanical factors, or improper foot alignment. Sports that involve running and jumping, footwear with high heels or a narrow toe box, and conditions such as hammertoes or Morton’s toe can increase the risk of developing capsulitis.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Patients with capsulitis may experience a dull pain or a feeling of instability around the ball of the foot and the base of the second toe. Diagnosis is usually made by a podiatrist through physical examination, reviewing medical history, and sometimes by imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs.
Treatment:
Conservative treatments for capsulitis include rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications, footwear modification, padding, and orthotics to relieve pressure on the affected area. Physical therapy exercises can also be beneficial in strengthening the surrounding muscles. In severe cases, when conservative measures fail, surgical intervention may be required.
Conclusion:
Capsulitis of the second metatarsophalangeal joint can be a painful condition that affects the foot’s functionality. Early recognition and appropriate treatment can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications. If you experience any foot pain or discomfort, it is essential to consult a podiatrist for proper diagnosis and management.